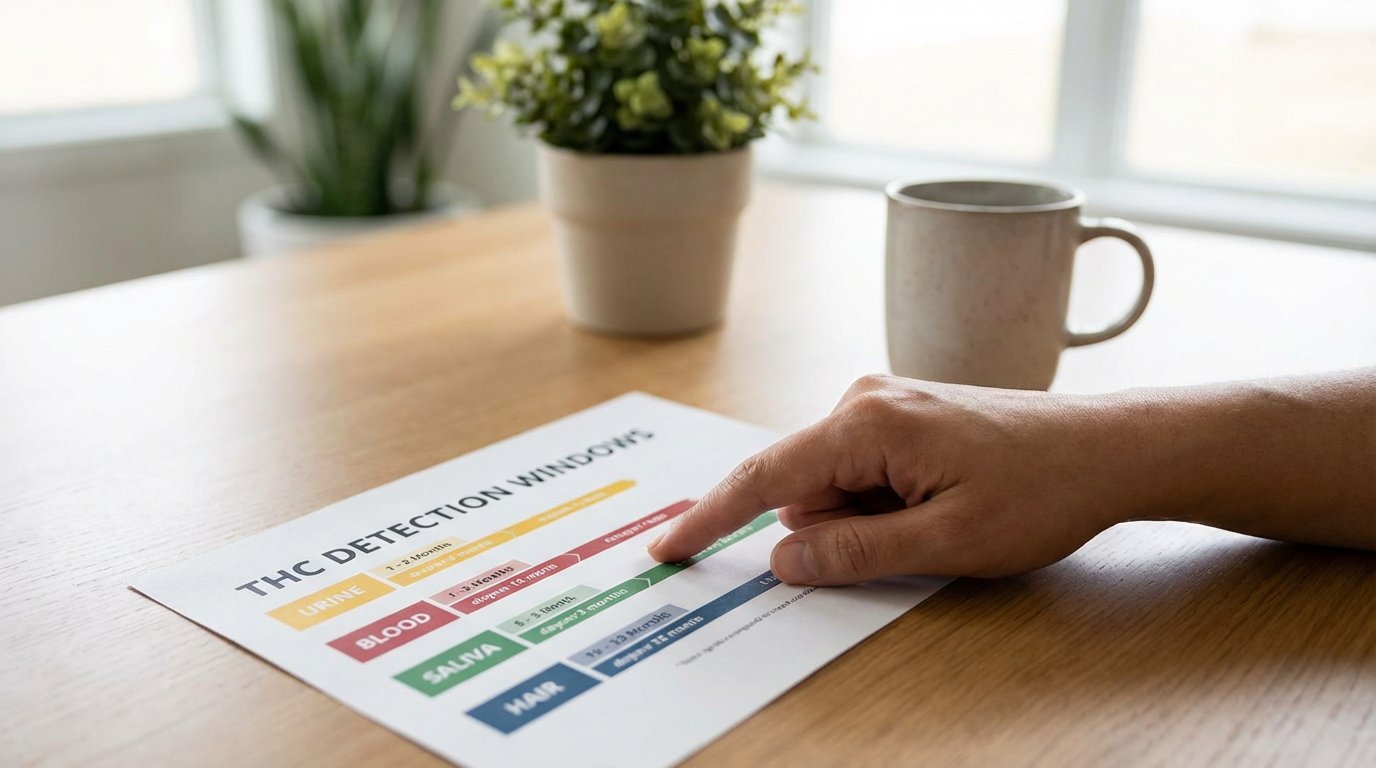
THC detection windows in your system vary considerably by test type:
saliva tests identify recent use within 24-72 hours,
urine tests detect metabolites for 3-30 days depending on usage frequency, blood tests measure active THC for 1-7 days, and
hair follicle analysis extends to 90 days. Your body fat percentage, metabolic rate, consumption method, and usage patterns directly influence elimination timelines. Standard urine screening uses a
50 ng/mL cutoff for THC-COOH metabolites. Understanding how your individual physiology, genetics, and the specific testing methodology interact will help you anticipate your results with greater precision.
Understanding THC Detection Windows Across Different Test Types
When selecting a
drug testing method for THC detection, you must consider the distinct
detection windows and
metabolite profiles each
specimen type offers. Urine tests identify THC metabolites, specifically THC-COOH, with detection windows spanning 1 to 30 days depending on chronic use patterns,
body composition, and metabolism rates. Saliva testing detects recent consumption within 24 hours, though test sensitivity varies by device technology.
Modern saliva tests demonstrate sensitivity of 79.4% and specificity of 98.3% when compared to blood tests.
Blood analysis measures active THC for 1 to 7 days, providing the most accurate assessment of recent use and potential impairment.
Blood testing can specifically detect the active, unmetabolized form of the drug rather than its breakdown products. Hair follicles offer extended detection up to 90 days but lack reliability for occasional use.
Most urine tests utilize a standard detection threshold of 50 ng/mL, though more sensitive laboratory tests can identify lower concentrations. Each method's effectiveness depends on factors including test sensitivity thresholds, your metabolic rate, body fat percentage, and consumption frequency, making specimen selection critical for accurate results.
Key Factors That Influence How Long THC Remains Detectable
Understanding the variables that determine
THC detectability requires examining the complex interplay between
biological, chemical, and analytical factors that govern
cannabinoid metabolism and elimination.
Frequency of use establishes baseline detection windows: single use yields detectable metabolites for approximately 3 days, while chronic heavy use extends this period to 30+ days as THC accumulates in adipose tissue. Your
body fat percentage directly influences retention, THC's lipophilic nature causes sequestration in fat cells, prolonging elimination in individuals with increased adipose mass.
Gender differences affect detection because women typically maintain higher body fat percentages than men. Once cannabis enters your bloodstream, metabolites undergo hepatic processing before urinary excretion. Test sensitivity thresholds and
analytical methods further modulate detection capabilities, with lower cutoff concentrations identifying cannabinoids at trace levels that standard assays miss. The quantity and
strength of marijuana consumed fundamentally determines how long THC remains in your system, with higher potency products leading to extended detection periods.
Faster metabolisms naturally process and eliminate THC more efficiently, reducing the overall detection window compared to individuals with slower metabolic rates.
Drug tests focus on identifying THC metabolites rather than the THC compound itself, as these by-products remain present in bodily fluids longer than the psychoactive effects last.
Saliva and Urine Testing: Most Common Screening Methods Explained
Because drug testing programs prioritize practical collection methods and varying
detection requirements,
saliva and urine tests have emerged as the two dominant
cannabis screening approaches in workplace, legal, and roadside contexts. Saliva testing detects THC in oral fluid for 24, 72 hours after occasional use, with roadside tests identifying recent consumption within 12, 30 hours depending on frequency. Smoking deposits more detectable residue than edibles, though eating or rinsing can reduce accuracy. The
detection window depends on test sensitivity and thoroughness of mouth swabbing. Saliva tests focus on
parent compounds like delta-9 THC rather than metabolites, which do not reliably transfer into oral fluid. Conversely,
urine testing identifies THC metabolites across extended detection timeframes: 3 days for single use, 5, 7 days for moderate consumption, and over 30 days for chronic users. While saliva tests confirm
recent impairment, urine analysis reveals
historical exposure without indicating current intoxication, making each method suitable for distinct screening objectives. Individual factors such as
metabolism and body composition can significantly influence how long THC remains detectable in both saliva and urine samples. Prescription medications and over the counter supplements can trigger
false positive results in urine tests, requiring confirmatory testing to verify cannabis use.
Blood and Hair Follicle Testing: What You Need to Know
Blood tests detect active THC in your system for 12 to 48 hours after consumption, though chronic users may test positive for 7 to 30 days in rare cases. These tests measure actual THC rather than metabolites, making them ideal for evaluating recent use and impairment in DUI cases or workplace accidents. Hair tests offer the longest detection window at 90 days, using a 1.5-inch cutoff from the scalp to identify chronic use patterns.
| Test Type |
Detection Window |
Measures |
Primary Use |
| Blood test |
12-48 hours (up to 30 days chronic use) |
Active THC |
Recent impairment evaluation |
| Hair test |
Up to 90 days |
THC metabolites |
Long-term use history |
Hair tests can produce false positives from passive exposure, while blood tests provide superior accuracy for recent consumption.
Test sensitivity plays a crucial role in determining whether THC or its metabolites will be detected in your system. Edibles are processed through
the digestive system and liver, which can extend detection windows compared to other consumption methods.
Saliva testing offers a shorter detection window of 24 to 72 hours, making it useful for identifying very recent cannabis use.
Additional Variables That Affect Your THC Detection Timeline
While
standard detection windows provide general guidance, your individual
THC elimination timeline depends on several interconnected
physiological and behavioral factors that create significant variability between users.
Body fat percentage and BMI directly influence retention duration since THC's lipophilic nature causes accumulation in adipose tissue. Genetics determine
liver enzyme efficiency, specifically CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 variants, which modulate metabolic rate and clearance speed.
Age and sex affect fat distribution patterns and baseline metabolism, impacting elimination kinetics. Diet and exercise can modestly alter metabolic processes, though effects remain limited.
Detection thresholds set by testing laboratories further complicate timelines; lower cutoff concentrations extend positive result windows while higher thresholds shorten them. The potency of cannabis consumed plays a crucial role, as
more potent cannabis with higher THC concentrations may remain detectable longer in your system. These variables interact complexly, making precise prediction challenging without considering your complete metabolic profile. When compulsive substance use quietly takes over your daily routine, your relationships, your focus, and your sense of self begin to fade in ways you may not even notice at first. Whether it is an unhealthy dependence on substances, obsessive behavioral patterns, or any other compulsive habit pulling you away from the life you want, the struggle is real and you do not have to face it alone. At
Pinnacle Detox and Recovery, we provide personalized addiction treatment, evidence-based therapy, and compassionate long-term recovery support tailored specifically to your needs and your journey.
Call +1 (626) 323-8629 today and take the first step toward lasting freedom.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Drinking Water or Detox Products Help Flush THC Faster?
Drinking water won't accelerate
THC elimination from your body, though it may dilute urine samples and temporarily lower metabolite concentrations.
Detox products lack peer-reviewed evidence supporting efficacy and function similarly to water alone. Your body's
metabolic rate, body fat percentage, and usage frequency determine clearance speed, not hydration or supplements. Excessive water intake risks producing dilute samples with abnormal
creatinine levels, triggering invalid test results rather than genuine THC removal. Natural physiological processes drive elimination, typically requiring days to weeks depending on individual factors.
Will Secondhand Marijuana Smoke Cause Me to Fail a Drug Test?
You're
highly unlikely to fail a drug test from secondhand marijuana smoke under normal circumstances.
Standard urine tests use a 50 ng/mL THC metabolite cutoff that's rarely reached through passive exposure. However, prolonged exposure in enclosed, poorly ventilated spaces with heavy smoke increases risk. Studies show THC from secondhand exposure typically clears your system within
24-72 hours. Blood, saliva, and hair tests are even less likely to detect passive exposure unless conditions are extreme.
Does CBD Show up on Standard Drug Tests for THC?
CBD itself won't trigger standard
THC drug tests, which target THC-COOH metabolites at a 50 ng/mL cutoff. However, you're at risk because many
CBD products contain trace THC due to contamination or legal hemp limits of 0.3%. Full-spectrum products pose higher risk than pure isolates. Since DOT and employers don't accept CBD as an excuse for positive results, you should avoid unregulated CBD products if you're subject to workplace drug screening.
Can I Pass a Drug Test Using Synthetic Urine Substitutes?
Synthetic urine can pass
standard immunoassay drug tests and basic specimen validity testing, as it mimics creatinine, pH, uric acid, and specific gravity. However, you're risking detection through
advanced LC-MS assays that identify missing endogenous markers like cotinine, urobilin, and cellular material. Labs increasingly employ
integrity checks beyond routine protocols.
Direct observation during collection, common in federal and military testing, makes substitution nearly impossible. Detection methods are evolving faster than synthetic formulations can adapt.
Do Employers Accept Medical Marijuana Cards as Valid Test Explanations?
Employers aren't
federally required to accept your
medical marijuana card as a valid test explanation, since cannabis remains illegal under federal law and the ADA excludes illegal drug use from protection. However, roughly half of states with medical marijuana programs have enacted
anti-discrimination protections for registered patients. Your employer's acceptance depends on your specific state law and workplace policy. Safety-sensitive positions, federal contractors, and federally regulated industries typically maintain
zero-tolerance policies regardless of your cardholder status.
 When selecting a drug testing method for THC detection, you must consider the distinct detection windows and metabolite profiles each specimen type offers. Urine tests identify THC metabolites, specifically THC-COOH, with detection windows spanning 1 to 30 days depending on chronic use patterns, body composition, and metabolism rates. Saliva testing detects recent consumption within 24 hours, though test sensitivity varies by device technology. Modern saliva tests demonstrate sensitivity of 79.4% and specificity of 98.3% when compared to blood tests. Blood analysis measures active THC for 1 to 7 days, providing the most accurate assessment of recent use and potential impairment. Blood testing can specifically detect the active, unmetabolized form of the drug rather than its breakdown products. Hair follicles offer extended detection up to 90 days but lack reliability for occasional use. Most urine tests utilize a standard detection threshold of 50 ng/mL, though more sensitive laboratory tests can identify lower concentrations. Each method's effectiveness depends on factors including test sensitivity thresholds, your metabolic rate, body fat percentage, and consumption frequency, making specimen selection critical for accurate results.
When selecting a drug testing method for THC detection, you must consider the distinct detection windows and metabolite profiles each specimen type offers. Urine tests identify THC metabolites, specifically THC-COOH, with detection windows spanning 1 to 30 days depending on chronic use patterns, body composition, and metabolism rates. Saliva testing detects recent consumption within 24 hours, though test sensitivity varies by device technology. Modern saliva tests demonstrate sensitivity of 79.4% and specificity of 98.3% when compared to blood tests. Blood analysis measures active THC for 1 to 7 days, providing the most accurate assessment of recent use and potential impairment. Blood testing can specifically detect the active, unmetabolized form of the drug rather than its breakdown products. Hair follicles offer extended detection up to 90 days but lack reliability for occasional use. Most urine tests utilize a standard detection threshold of 50 ng/mL, though more sensitive laboratory tests can identify lower concentrations. Each method's effectiveness depends on factors including test sensitivity thresholds, your metabolic rate, body fat percentage, and consumption frequency, making specimen selection critical for accurate results.
 Because drug testing programs prioritize practical collection methods and varying detection requirements, saliva and urine tests have emerged as the two dominant cannabis screening approaches in workplace, legal, and roadside contexts. Saliva testing detects THC in oral fluid for 24, 72 hours after occasional use, with roadside tests identifying recent consumption within 12, 30 hours depending on frequency. Smoking deposits more detectable residue than edibles, though eating or rinsing can reduce accuracy. The detection window depends on test sensitivity and thoroughness of mouth swabbing. Saliva tests focus on parent compounds like delta-9 THC rather than metabolites, which do not reliably transfer into oral fluid. Conversely, urine testing identifies THC metabolites across extended detection timeframes: 3 days for single use, 5, 7 days for moderate consumption, and over 30 days for chronic users. While saliva tests confirm recent impairment, urine analysis reveals historical exposure without indicating current intoxication, making each method suitable for distinct screening objectives. Individual factors such as metabolism and body composition can significantly influence how long THC remains detectable in both saliva and urine samples. Prescription medications and over the counter supplements can trigger false positive results in urine tests, requiring confirmatory testing to verify cannabis use.
Because drug testing programs prioritize practical collection methods and varying detection requirements, saliva and urine tests have emerged as the two dominant cannabis screening approaches in workplace, legal, and roadside contexts. Saliva testing detects THC in oral fluid for 24, 72 hours after occasional use, with roadside tests identifying recent consumption within 12, 30 hours depending on frequency. Smoking deposits more detectable residue than edibles, though eating or rinsing can reduce accuracy. The detection window depends on test sensitivity and thoroughness of mouth swabbing. Saliva tests focus on parent compounds like delta-9 THC rather than metabolites, which do not reliably transfer into oral fluid. Conversely, urine testing identifies THC metabolites across extended detection timeframes: 3 days for single use, 5, 7 days for moderate consumption, and over 30 days for chronic users. While saliva tests confirm recent impairment, urine analysis reveals historical exposure without indicating current intoxication, making each method suitable for distinct screening objectives. Individual factors such as metabolism and body composition can significantly influence how long THC remains detectable in both saliva and urine samples. Prescription medications and over the counter supplements can trigger false positive results in urine tests, requiring confirmatory testing to verify cannabis use.
 While standard detection windows provide general guidance, your individual THC elimination timeline depends on several interconnected physiological and behavioral factors that create significant variability between users. Body fat percentage and BMI directly influence retention duration since THC's lipophilic nature causes accumulation in adipose tissue. Genetics determine liver enzyme efficiency, specifically CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 variants, which modulate metabolic rate and clearance speed. Age and sex affect fat distribution patterns and baseline metabolism, impacting elimination kinetics. Diet and exercise can modestly alter metabolic processes, though effects remain limited. Detection thresholds set by testing laboratories further complicate timelines; lower cutoff concentrations extend positive result windows while higher thresholds shorten them. The potency of cannabis consumed plays a crucial role, as more potent cannabis with higher THC concentrations may remain detectable longer in your system. These variables interact complexly, making precise prediction challenging without considering your complete metabolic profile. When compulsive substance use quietly takes over your daily routine, your relationships, your focus, and your sense of self begin to fade in ways you may not even notice at first. Whether it is an unhealthy dependence on substances, obsessive behavioral patterns, or any other compulsive habit pulling you away from the life you want, the struggle is real and you do not have to face it alone. At Pinnacle Detox and Recovery, we provide personalized addiction treatment, evidence-based therapy, and compassionate long-term recovery support tailored specifically to your needs and your journey. Call +1 (626) 323-8629 today and take the first step toward lasting freedom.
While standard detection windows provide general guidance, your individual THC elimination timeline depends on several interconnected physiological and behavioral factors that create significant variability between users. Body fat percentage and BMI directly influence retention duration since THC's lipophilic nature causes accumulation in adipose tissue. Genetics determine liver enzyme efficiency, specifically CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 variants, which modulate metabolic rate and clearance speed. Age and sex affect fat distribution patterns and baseline metabolism, impacting elimination kinetics. Diet and exercise can modestly alter metabolic processes, though effects remain limited. Detection thresholds set by testing laboratories further complicate timelines; lower cutoff concentrations extend positive result windows while higher thresholds shorten them. The potency of cannabis consumed plays a crucial role, as more potent cannabis with higher THC concentrations may remain detectable longer in your system. These variables interact complexly, making precise prediction challenging without considering your complete metabolic profile. When compulsive substance use quietly takes over your daily routine, your relationships, your focus, and your sense of self begin to fade in ways you may not even notice at first. Whether it is an unhealthy dependence on substances, obsessive behavioral patterns, or any other compulsive habit pulling you away from the life you want, the struggle is real and you do not have to face it alone. At Pinnacle Detox and Recovery, we provide personalized addiction treatment, evidence-based therapy, and compassionate long-term recovery support tailored specifically to your needs and your journey. Call +1 (626) 323-8629 today and take the first step toward lasting freedom.