Common behavioral addictions in 2025 include
internet dependency (affecting one-third of the global population),
gambling disorder (prevalent in 38 U.S. states),
compulsive shopping (5-8% worldwide), and
social media addiction (51% of Gen Z users report constant usage). You'll also encounter exercise addiction, food-related compulsions, and emerging digital dependencies like AI chatbot attachment and cryptocurrency trading obsession. Understanding these patterns and their warning signs can help you identify potential risks in your daily life.
The Rise of Internet and Digital Dependencies
Internet and
digital dependencies have exploded into a
global health crisis, with over one-third of the world's population now exhibiting signs of
internet addiction. You'll find this reflected in stark statistics: 36.7% of people are addicted to the internet, while another 33.9% show moderate addiction symptoms. As
internet governance initiatives struggle to keep pace, approximately 210 million individuals globally battle digital dependencies. Gen Z adults are particularly vulnerable, with
51% using social media constantly. The crisis is particularly acute in
social media usage, where 56.8% of the world's population actively engages.
Digital well-being frameworks are becoming essential as platforms like TikTok, YouTube, and Facebook demonstrate unprecedented addictive potential. TikTok users alone spend an average of 34 hours monthly online, while 51% of U.S. teens dedicate nearly five hours daily to social media consumption. The average person now spends
nine hours daily in front of screens, highlighting the pervasive nature of digital consumption in modern life. Studies show
validation-seeking behaviors through likes and comments reinforce these addictive patterns across all social platforms.
Gambling Behavior in the Modern Era
While digital dependencies dominate modern behavioral addiction discussions, gambling disorder has emerged as a comparably pervasive public health challenge. You'll find that modern gambling's accessibility has transformed dramatically, with 38 states now permitting sports betting and 28% of Americans gambling online daily. Young adults aged 18-34 face heightened risks, with an astounding
90% believing they can consistently profit from sports betting. Recent data shows that nearly
one quarter of sports bettors have failed to pay their bills due to gambling losses.
Slot machines remain the greatest risk, with three-quarters of problem gamblers primarily playing slots.
| Key Risk Factors |
Statistics |
Impact |
| Gender Disparity |
Men 2x more likely |
Higher intervention needs |
| Life Stage Demographics |
48% men 18-49 betting |
Targeted policy responses |
| Online Access |
81% problem gamblers prefer |
Public health concerns |
Problem gambling intervention has become increasingly critical as only 8% of the 5 million affected Americans seek help. Public health policy responses must address the stark reality that between 30-50% of U.S. gamblers struggle with problematic behavior, while mobile sports betting continues driving unprecedented demand for addiction support services.
The
compulsion to shop excessively affects a considerable portion of the global population, with prevalence rates ranging from 5-8% worldwide. You'll find striking
shopping addiction gender differences, with women representing 90% of reported cases, typically emerging in late teens to early twenties. Those with
untreated mental illness face higher risks of developing shopping addiction. Recent data shows Americans spend
$4.8 trillion annually on retail purchases. The behavior follows a distinctive pattern: anticipation, preparation, the "thrill of the hunt," and spending, often followed by regret.
Shopping related financial consequences can be severe; you're four times less likely to pay off credit cards if you're dealing with this addiction. The rise of 24/7 online shopping access has intensified these patterns. Individuals experiencing shopping addiction often accumulate significant
credit card debt and loans, leading to potential bankruptcy. The condition frequently
co-occurs with depression, anxiety, and substance use disorders, using shopping as a coping mechanism for negative emotions.
Social media exposure, particularly excessive Facebook use, can substantially increase your risk.
Sexual Behavior Addictions and Their Impact
Although often stigmatized and misunderstood,
sexual behavior addictions affect a substantial portion of the U.S. adult population, with
prevalence rates ranging from 3% to 6%.
Men are disproportionately affected, with ratios up to 5:1 compared to women. International studies indicate that
cognitive behavioral therapy shows the most promising results for treatment. Most individuals delay seeking help until their
late thirties, allowing destructive patterns to become deeply ingrained. Several risk factors for sexual behavior addictions have been identified, including
early exposure to internet pornography, childhood trauma, and dysfunctional family dynamics. Research shows that
solo porn use can increase divorce rates from 6% to 11% when individuals begin viewing after marriage. A striking 31% of affected individuals report histories of
sexual abuse, while 34%-71% struggle with concurrent substance use disorders. The impact on intimate relationships is severe, with 46% experiencing sexual dysfunction. You'll find these behaviors often lead to relationship strain,
eroded trust, and diminished sexual satisfaction. The disorder typically persists for decades before treatment, complicated by high rates of depression (58%) and intense feelings of shame.
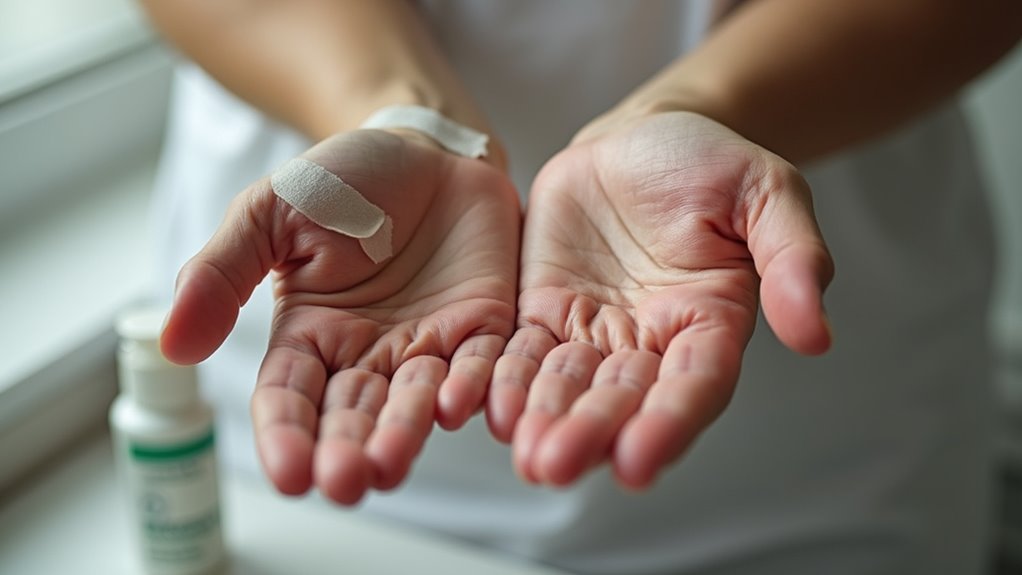
Skin Picking and Self-Harm Behaviors
Research indicates that skin picking disorder (SPD) affects approximately 2.1% of the general population, with lifetime prevalence rates reaching 3.1%. You'll find this condition manifests through repetitive picking, scratching, or squeezing behaviors, typically occurring 2-3 times daily in 10-30 minute episodes. Studies show that
anxiety and depression frequently accompany SPD as common mental health comorbidities. The most common areas targeted are
facial regions and upper extremities. The MGH Excoriation Clinic and Research Unit provides
state-of-the-art treatments for individuals struggling with this disorder.
| Aspect |
Clinical Characteristics |
| Treatment Approaches |
CBT, Habit Reversal Training |
| Prevention Strategies |
Stress Management, Trigger Identification |
| Risk Factors |
Genetic Predisposition, Trauma History |
Understanding SPD's distinction from self-harm is essential, as it's not typically performed with conscious self-injury intent. However, both conditions require specialized mental health interventions. Treatment approaches focus on cognitive behavioral therapy and habit reversal training, while prevention strategies emphasize stress management and early identification of triggers. The condition shows higher prevalence in females and frequently co-occurs with other obsessive-compulsive spectrum disorders.
While
food addiction remains absent from the DSM-5's official classifications, compelling evidence shows it affects 5-10% of the general population, with particularly high rates among individuals struggling with
obesity and eating disorders. You'll encounter several distinct patterns of problematic eating, including
compulsive snacking behaviors,
binge eating, and night eating syndrome. Research reveals food reward processing abnormalities in affected individuals, mirroring brain changes seen in substance use disorders. Your
brain's reward pathways, particularly those involving dopamine, can become altered when repeatedly exposed to highly palatable foods. If you're experiencing these patterns, you're not alone; studies show that 38% of adults report
stress-related overeating, and food cravings affect up to 100% of young women and 70% of young men annually.
Exercise and Fitness Obsessions
While 3% of regular exercisers develop
exercise addiction, you'll notice key
warning signs, including persistent training despite injuries, withdrawal symptoms when unable to exercise, and organizing your entire life around workout schedules. You're at higher risk if you're a
competitive athlete, young adult, or someone with underlying body image concerns, as research shows these populations experience addiction rates of up to 42%. If you recognize these patterns, effective
recovery strategies include working with mental health professionals, gradually modifying exercise routines, and addressing any
co-occurring conditions like depression or anxiety, which affect over 70% of those with exercise addiction.
Compulsive Training Warning Signs
Although
regular exercise promotes physical and mental well-being, compulsive training behaviors can signal a dangerous
behavioral addiction that requires intervention.
Exercise dependence monitoring becomes pivotal when you notice these
warning signs of an
excessive fitness regime:
- You consistently train more than 600 minutes weekly, ignoring injuries and medical advice while experiencing withdrawal symptoms when unable to exercise
- Your self-worth depends entirely on workout performance, leading to anxiety, depression, and intense guilt when missing sessions
- You're isolating yourself from relationships and responsibilities to maintain rigid exercise schedules, often training in secret
These behaviors indicate a shift from healthy fitness habits to addiction, potentially causing severe physical consequences like
chronic injuries, hormonal disruption, and nutritional deficiencies. Early recognition of these patterns is essential for
successful intervention.
Gym Addiction Recovery Strategies
Once warning signs of exercise addiction are identified, implementing structured recovery strategies becomes the next step in the direction of healing. Evidence-based practices emphasize a multidisciplinary treatment model that combines physical and psychological interventions.
| Recovery Component |
Implementation Strategy |
| Exercise Planning |
FITT principle with medical clearance |
| Psychological Support |
CBT and motivation boosting |
| Social Integration |
Peer support groups and team activities |
| Relapse Prevention |
Self-efficacy building and trigger management |
You'll need to work with healthcare providers to create a balanced recovery ecosystem that addresses both physical and mental aspects of addiction. This includes customizing exercise plans within safe limits, engaging in cognitive-behavioral therapy, and participating in support groups. The approach focuses on developing sustainable habits while preventing overtraining through regular monitoring and adjustment of your recovery goals.
Social Media Usage and Content Creation Compulsions
Your brain's
reward system responds powerfully to social media engagement through
dopamine releases triggered by likes, shares, and comments, creating a neurological basis for addictive posting behaviors. You'll find yourself caught in
validation-seeking cycles, where the drive to create and share content becomes compulsive as algorithms reinforce your digital interaction patterns. As a content creator, you're especially vulnerable to these compulsions, with research showing creators can spend up to 9 hours daily posting and engaging, far exceeding typical usage patterns and indicating a clear shift from healthy engagement to
behavioral addiction.
Dopamine-Driven Posting Behaviors
The widespread prevalence of
dopamine-driven posting behaviors has emerged as a
considerable behavioral addiction, affecting approximately 210 million people worldwide. You'll notice these behaviors manifesting through
constant device checking,
compulsive content creation, and
intense social comparison behaviors that trigger
dopamine feedback loops. Research indicates concerning patterns among social media users:
- Up to 70% of teens and young adults report addiction symptoms, spending an average of 4.8 hours daily on platforms
- TikTok users consume 34 hours monthly, while YouTube users average 28 hours
- 51% of teenagers exhibit compulsive posting patterns, driven by engineered engagement features
These statistics reveal how platform algorithms intensify addictive posting behaviors by leveraging notifications, social rewards, and curated content feeds. The resulting
dopamine-driven compulsions substantially impact mental health, particularly among younger demographics.
Digital Validation Seeking Patterns
Building upon
dopamine-driven behaviors,
digital validation seeking has emerged as a distinct psychological pattern affecting over 1.54 billion social media users worldwide. You'll find yourself caught in
algorithmic validation loops, where platforms strategically amplify your need for likes and comments through
targeted content curation. Social platform incentive structures now shape your self-worth estimation, with 70% of teens and young adults displaying
problematic usage patterns. You're likely spending a significant portion of your 4.8 daily social media hours seeking digital approval, reinforced by
unpredictable reward cycles similar to gambling mechanics. This behavior manifests through compulsive posting, story sharing, and constant feedback monitoring. The impact is particularly severe during developmental years, as you internalize online engagement metrics as personal success indicators.
Compulsive Content Creation Cycles
While social media platforms revolutionized digital communication, they've spawned widespread
compulsive content creation affecting an estimated 210 million users worldwide by 2025. Your daily cycle of posting, sharing, and seeking engagement triggers
dopamine-driven feedback loops similar to substance addictions, leading to
content creation burnout and serious
mental health consequences. Key indicators of compulsive content creation include:
- Spending 4.8+ hours daily creating and sharing content
- Inability to pause posting for several hours without experiencing anxiety
- Disrupted sleep patterns and decreased concentration from constant platform engagement
You're particularly vulnerable if you're among the 51% of teens heavily invested in platforms like TikTok, YouTube, or Facebook. The
validation-seeking behavior intensifies through
algorithmic reinforcement, often resulting in academic decline, increased anxiety, and depression.
Emerging Behavioral Addiction Trends
Recent technological advances and societal shifts have dramatically reshaped the terrain of
behavioral addictions, with emerging trends pointing to an increasingly
digital-centric pattern of compulsive behaviors. You'll notice significant changes in how behavioral addictions manifest, particularly with
AI chatbot dependence becoming a concerning phenomenon. Users increasingly form emotional attachments to conversational AI, seeking constant digital companionship for psychological support. Likewise,
cryptocurrency trading obsession has emerged as a distinct behavioral pattern, characterized by compulsive market monitoring and high-risk trading behaviors. Short-form video platforms and
VR immersion are creating novel addiction patterns, while
wearable device overuse reflects our growing dependence on constant biometric feedback. These emerging trends often intersect with
post-pandemic isolation and hybrid work models, amplifying their impact on daily functioning.
From the compulsive need to check your phone every few minutes, to uncontrollable urges around food, work, or spending, behavioral addiction shows up in more ways than most people realize. What starts as a coping mechanism slowly grows into something that controls your thoughts, disrupts your relationships, and drains your sense of self. At Pinnacle Detox and Recovery, we provide personalized behavioral addiction treatment, targeted therapy, and long-term recovery support designed to help you identify the root of your struggle and break free from it for good. Call +1 (626) 323-8629 today and take the first step toward lasting change.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do Genetic Factors Influence Susceptibility to Behavioral Addictions?
Your
genetic predisposition substantially influences your vulnerability to
behavioral addictions, with heritability rates ranging from 40-60%. You're more susceptible if you've inherited specific variants of genes affecting
dopamine and serotonin systems, which control reward and pleasure responses. When these genetic factors interact with environmental triggers, like stress or trauma, you'll face an elevated risk. Your
family history can make you particularly vulnerable to developing multiple types of behavioral dependencies.
What Role Does Childhood Trauma Play in Developing Multiple Behavioral Addictions?
If you've experienced
childhood emotional neglect or
physical abuse, you're at considerably higher risk for developing
multiple behavioral addictions. Your early trauma can alter your brain's reward circuits and executive function, making you more susceptible to compulsive behaviors. You'll often see this manifested through co-occurring addictions like gambling, internet use, or shopping.
Trauma-induced changes to your dopamine signaling and stress response systems can intensify your vulnerability to multiple addictive patterns simultaneously.
Can Behavioral Addictions Be Completely Cured or Only Managed Long-Term?
You can't completely cure
behavioral addictions, but you can effectively manage them long-term. Your brain's reward circuits remain permanently altered, making you vulnerable to relapse even after extended periods of abstinence. You'll need to focus on
long-term management strategies like CBT, support groups, and digital monitoring tools. Implementing
relapse prevention techniques and maintaining ongoing therapeutic support will help you achieve sustained remission rather than expecting a permanent cure.
Are Certain Professions More Vulnerable to Specific Behavioral Addictions?
Yes, your profession can vastly impact your vulnerability to
behavioral addictions. High stress occupations often present specific risk factors: finance professionals face heightened
gambling disorder risks, while tech workers show higher rates of
internet and smartphone addiction. Healthcare workers are more prone to
work addiction, and law enforcement personnel frequently develop gambling issues. Your occupational environment, stress levels, and daily exposure to certain activities directly influence addiction susceptibility.
How Effective Is Group Therapy Compared to Individual Treatment?
Group therapy proves comparable or more beneficial than
individual treatment for behavioral addictions, offering unique advantages through shared experiences and increased engagement. You'll find that
meta-analyses show comparable or superior symptom reduction, particularly for
gambling and gaming disorders. Through
social learning and peer support, you'll benefit from improved coping strategies and reduced isolation. While both approaches work, you'll often achieve ideal outcomes when combining group and individual therapy modalities.
 Internet and digital dependencies have exploded into a global health crisis, with over one-third of the world's population now exhibiting signs of internet addiction. You'll find this reflected in stark statistics: 36.7% of people are addicted to the internet, while another 33.9% show moderate addiction symptoms. As internet governance initiatives struggle to keep pace, approximately 210 million individuals globally battle digital dependencies. Gen Z adults are particularly vulnerable, with 51% using social media constantly. The crisis is particularly acute in social media usage, where 56.8% of the world's population actively engages. Digital well-being frameworks are becoming essential as platforms like TikTok, YouTube, and Facebook demonstrate unprecedented addictive potential. TikTok users alone spend an average of 34 hours monthly online, while 51% of U.S. teens dedicate nearly five hours daily to social media consumption. The average person now spends nine hours daily in front of screens, highlighting the pervasive nature of digital consumption in modern life. Studies show validation-seeking behaviors through likes and comments reinforce these addictive patterns across all social platforms.
Internet and digital dependencies have exploded into a global health crisis, with over one-third of the world's population now exhibiting signs of internet addiction. You'll find this reflected in stark statistics: 36.7% of people are addicted to the internet, while another 33.9% show moderate addiction symptoms. As internet governance initiatives struggle to keep pace, approximately 210 million individuals globally battle digital dependencies. Gen Z adults are particularly vulnerable, with 51% using social media constantly. The crisis is particularly acute in social media usage, where 56.8% of the world's population actively engages. Digital well-being frameworks are becoming essential as platforms like TikTok, YouTube, and Facebook demonstrate unprecedented addictive potential. TikTok users alone spend an average of 34 hours monthly online, while 51% of U.S. teens dedicate nearly five hours daily to social media consumption. The average person now spends nine hours daily in front of screens, highlighting the pervasive nature of digital consumption in modern life. Studies show validation-seeking behaviors through likes and comments reinforce these addictive patterns across all social platforms.
 The compulsion to shop excessively affects a considerable portion of the global population, with prevalence rates ranging from 5-8% worldwide. You'll find striking shopping addiction gender differences, with women representing 90% of reported cases, typically emerging in late teens to early twenties. Those with untreated mental illness face higher risks of developing shopping addiction. Recent data shows Americans spend $4.8 trillion annually on retail purchases. The behavior follows a distinctive pattern: anticipation, preparation, the "thrill of the hunt," and spending, often followed by regret. Shopping related financial consequences can be severe; you're four times less likely to pay off credit cards if you're dealing with this addiction. The rise of 24/7 online shopping access has intensified these patterns. Individuals experiencing shopping addiction often accumulate significant credit card debt and loans, leading to potential bankruptcy. The condition frequently co-occurs with depression, anxiety, and substance use disorders, using shopping as a coping mechanism for negative emotions. Social media exposure, particularly excessive Facebook use, can substantially increase your risk.
The compulsion to shop excessively affects a considerable portion of the global population, with prevalence rates ranging from 5-8% worldwide. You'll find striking shopping addiction gender differences, with women representing 90% of reported cases, typically emerging in late teens to early twenties. Those with untreated mental illness face higher risks of developing shopping addiction. Recent data shows Americans spend $4.8 trillion annually on retail purchases. The behavior follows a distinctive pattern: anticipation, preparation, the "thrill of the hunt," and spending, often followed by regret. Shopping related financial consequences can be severe; you're four times less likely to pay off credit cards if you're dealing with this addiction. The rise of 24/7 online shopping access has intensified these patterns. Individuals experiencing shopping addiction often accumulate significant credit card debt and loans, leading to potential bankruptcy. The condition frequently co-occurs with depression, anxiety, and substance use disorders, using shopping as a coping mechanism for negative emotions. Social media exposure, particularly excessive Facebook use, can substantially increase your risk.
 Research indicates that skin picking disorder (SPD) affects approximately 2.1% of the general population, with lifetime prevalence rates reaching 3.1%. You'll find this condition manifests through repetitive picking, scratching, or squeezing behaviors, typically occurring 2-3 times daily in 10-30 minute episodes. Studies show that anxiety and depression frequently accompany SPD as common mental health comorbidities. The most common areas targeted are facial regions and upper extremities. The MGH Excoriation Clinic and Research Unit provides state-of-the-art treatments for individuals struggling with this disorder.
Research indicates that skin picking disorder (SPD) affects approximately 2.1% of the general population, with lifetime prevalence rates reaching 3.1%. You'll find this condition manifests through repetitive picking, scratching, or squeezing behaviors, typically occurring 2-3 times daily in 10-30 minute episodes. Studies show that anxiety and depression frequently accompany SPD as common mental health comorbidities. The most common areas targeted are facial regions and upper extremities. The MGH Excoriation Clinic and Research Unit provides state-of-the-art treatments for individuals struggling with this disorder.